 Floating Filters
Floating Filters
Floating Filters are an additional row under the column headers where the user will be able to see and optionally edit
the filters associated with each column.
Floating filters are activated by setting the Column Property floatingFilter = True:
columnDefs = [
{
'field': 'country',
'filter': True,
'floatingFilter': True
},
]
To have floating filters on for all columns by default, you should set floatingFilter on the defaultColDef. You can
then disable floating filters on a per-column basis by setting floatingFilter = False on an individual Column
Definition.
Floating filters depend on and co-ordinate with the main column filters. They do not have their own state, but rather
display the state of the main filter and set state on the main filter if they are editable. For this reason, there is
no API for getting or setting state of the floating filters.
Every floating filter takes a parameter to show/hide automatically a button that will open the main filter.
To see how floating filters work
see Floating Filter Components.
The following example shows the following features of floating filters:
- Text filter: has out of the box read/write floating filter (Sport, Country and Sport columns)
- Date and Number filter: have out of the box read/write floating filters for all filters except when switching to
in-range
filtering, where the floating filter is read-only (Age and Date columns) - Columns with buttons containing ‘apply’ require the user to press <kbd>↵ Enter<kbd> on the floating filter for the
filter to take effect (Gold column). (Note: this does not apply to floating Date Filters, which are always applied
as soon as a valid date is entered.) - Changes made directly to the main filter are reflected automatically in the floating filters (change any main filter)
- The user can configure when to show/hide the button that shows the full filter (Silver and Bronze columns)
- The Year column has a filter, but has the floating filter disabled
- The Total column has no filter and therefore no floating filter either
- Combining
suppressHeaderMenuButton = Trueandfilter = Falselets you control where the user can access the full filter. In
this examplesuppressHeaderMenuButton = Truefor all the columns except Year, Silver, Bronze and Total
```python
import dash_ag_grid as dag
from dash import Dash, html
import pandas as pd
app = Dash()
df = pd.read_csv(
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/plotly/datasets/master/ag-grid/olympic-winners.csv"
)
columnDefs = [
{"field": "athlete", "filter": "agTextColumnFilter", "suppressHeaderMenuButton": True},
{"field": "age", "filter": "agNumberColumnFilter", "suppressHeaderMenuButton": True},
{"field": "country", "filter": "agTextColumnFilter", "suppressHeaderMenuButton": True},
{"field": "year", "filter": "agNumberColumnFilter", "floatingFilter": False},
{
"field": 'date', "filter": 'agDateColumnFilter', "suppressHeaderMenuButton": True,
"filterParams": {
"comparator": {"function": "dateComparator"}
}
},
{"field": "sport", "filter": "agTextColumnFilter", "suppressHeaderMenuButton": True},
{
"field": "gold", "filter": "agNumberColumnFilter", "suppressHeaderMenuButton": True,
"filterParams": {
"buttons": ["apply"],
},
},
{
"field": "silver", "filter": "agNumberColumnFilter",
"suppressFloatingFilterButton": True,
},
{
"field": "bronze", "filter": "agNumberColumnFilter",
"suppressFloatingFilterButton": True,
},
{"field": "total", "filter": False},
]
app.layout = html.Div(
[
dag.AgGrid(
id="floating-filter-example",
rowData=df.to_dict("records"),
columnDefs=columnDefs,
defaultColDef={"flex": 1, "minWidth": 150, "filter": True, "floatingFilter": True},
)
]
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)
```
Provided Floating Filters
All the default filters provided by the grid provide their own implementation of a floating filter. All you need to do
to enable these floating filters is set the column property the floatingFilter = True. The features of the provided
floating filters are as follows:
| Filter | Editable | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Text | Sometimes | Provides a text input field to display the filter value, or a read-only label if read-only. |
| Number | Sometimes | Provides a text input field to display the filter value (unless using Custom Number Support), or a read-only label if read-only. |
| Date | Sometimes | Provides a date input field to display the filter value, or a read-only label if read-only. |
| Set | No | Provides a read-only label by concatenating all selected values. |
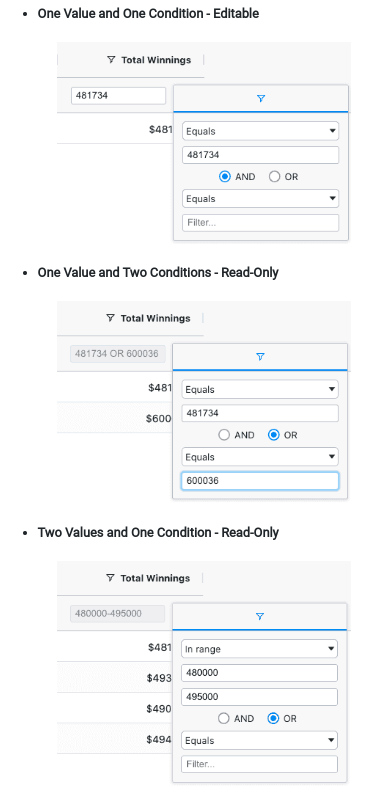
The floating filters for Text, Number and Date (the simple filters) are editable when the filter has one condition and
one value. If the floating filter has a) two conditions or b) zero (custom option) or two (‘In Range’) values, the
floating filter is read-only.
The screenshots below show example scenarios where the provided Number floating filter is editable and read-only.
Custom Floating Filters
In addition to the floating filters provided by the grid, you can also create your own
Custom Floating Filter Components.