 Row Models
Row Models
The grid can be configured with different strategies for loading row data into the grid, which are encapsulated into
different Row Models. Changing which Row Model the grid is using means changing
the strategy the grid is using for loading rows.
The grid comes with four row models:
- Client-Side
- Server-Side
- Infinite
- Viewport
The Client-Side Row Model deals with client-side data. The Server-Side, Infinite and Viewport Row Models deal with
server-side data. The following is a summary of each:
Client-Side
This is the default. The grid will load all the data into the grid in one go. The grid can then perform filtering,
sorting, grouping, pivoting and aggregation all in memory. Go
to Client-Side Row Model
Infinite
This will present the data to the user and load more data as the user scrolls down. Use this if you want to display a
large, flat (not grouped) list of data. Go
to Infinite Row Model
Server-Side (Enterprise)
The Server-Side Row Model builds on the Infinite Row Model. In addition to lazy-loading the data as the user scrolls
down, it also allows lazy-loading of grouped data with server-side grouping and aggregation. Advanced users will use
Server-Side Row Model to do ad-hoc slice and dice of data with server-side aggregations. Go
to Server-Side Row Model(AG Grid Docs)
Viewport (Enterprise)
The grid will inform the server exactly what data it is displaying (first and last row) and the server will provide data
for exactly those rows only. Use this if you want the server to know exactly what the user is viewing, useful for
updates in very large live datastreams where the server only sends updates to clients viewing the impacted rows. Go
to Viewport Row Model (AG Grid Docs)
When to Use
To help you to decide which row model to use, here’s some advice from
the Official AG Grid Docs:
Which row model you use will depend on your application. Here are some quick rules of thumb:
- If using AG Grid Community, use Client-Side if you want
to load all your data into the browser, or Infinite
if you want to load it in blocks.- If using AG Grid Enterprise, use Client-Side Row Model
if you want to load all your data into the browser,
or Server-Side if you
want to load it in blocks. Server-Side Row Model is Infinite Row Model plus more. So if you are an AG Grid
Enterprise customer, you should prefer Server-Side Row Model over Infinite Row Model.- Don’t use Viewport unless you
understand what its advantages are and when you need them. We find many of our users use Viewport Row Model when
they don’t need to and end up with more complicated applications as a result.Here are more detailed rules of thumb.
- If you are not sure, use default Client-Side. The grid can
handle massive amounts of data (100k+ rows). The grid will only render what’s visible on the screen (40 rows
approximately, depending on your screen size) even if you have thousands of rows returned from your server. You will
not kill the grid with too much data - rather your browser will run out of memory before the grid gets into
problems.
So if you are unsure, go with Client-Side first and only change if you need to. With Client-Side, you get sorting,
filtering, grouping, pivoting and aggregation all done for you by the grid. All the examples in the documentation
use the Client-Side unless specified otherwise.- If you do not want to shift all the data from your server to your client, as the amount of data is too large to
shift over the network or to extract from the underlying datasource, then use either Infinite, Server-Side or
Viewport. Each one takes data from the server in different ways.- Use Infinite
or Server-Side to bring
back a list of data one block at a time from the server. As the user scrolls, the grid will ask for more rows.
Server-Side has more features than Infinite and will allow row grouping, aggregation, lazy-loading of groups and
slice and dice of data.- Use Viewport
if you want the server to know exactly what the user is looking at. This is best when you have a large amount of
changing data and want to push updates to the client when the server-side data changes. Knowing exactly what the
user is looking at means you only have to push updates to the relevant users. All the row models can receive updates
but only the Viewport row model provides the server with the information of the rows the users currently sees on
screen without scrolling.
Row Model Comparisons
See the AG Grid docs Row Models
section for a feature comparison of all the grid’s features across all four row models.
Deeper Understanding of Row Models
The grid follows an MVC pattern. Each data item is wrapped in a Row Node and then stored in the Row Model. The
grid rendering engine is called Row Renderer and listens for changes to the row model and updates the DOM
accordingly.
Below shows a simplified version of a class diagram showing the relationships between the major classes involved with
the row models.
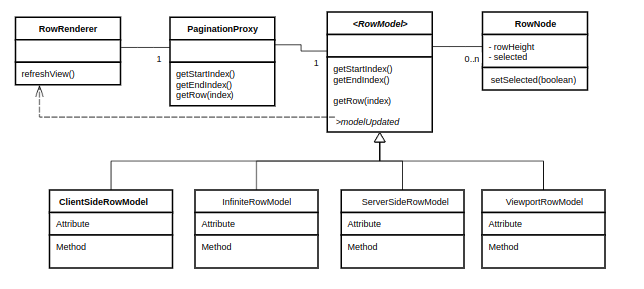
The following should be noted from the diagram:
- The grid has exactly one
RowRendererinstance. TheRowRenderercontains a reference to thePaginationProxywhere
it asks for the rows one at a time for rendering. - The grid has exactly one
PaginationProxyinstance. ThePaginationProxywill either a) do nothing if pagination is
not active and just forward all requests to the Row Model or b) do pagination if pagination is active.
ThePaginationProxyhas exactly oneRowModelinstance. - You can configure the grid to use any of the provided Row Models - that’s why
RowModelis in italics, it means
it’s an interface, the concrete implementation is what you decide when configuring the grid. TheRowModelcontains a
list ofRowNodes. TheRowModelmay have a list of all theRowNodes(Client-Side Row Model) or have a datasource
where it can lazy-loadRowNodes. - A RowNode has a reference to exactly one row data item (the client application provides the row data items).
TheRowNodehas state information about the row item, such as whether it is selected and the height of it. - When there is a change of state in the
RowNodes, theRowModelfires a modelUpdated event which gets
theRowRendererto refresh. This happens for many reasons, for example, the data is sorted, filtered, a group is
opened, or the underlying data has changed.
Pagination
Pagination can be applied to any of the row model types. The documentation on each row model type covers pagination for
that row model type.
<br>